
Key Challenges in Achieving PDPA Compliance in 2024
June 14, 2024






A. Importance of Data Protection in Singapore
In today's hyper-connected world, the importance of data protection has never been greater. For businesses operating in Singapore, the stakes are exceptionally high due to the nation's advanced digital infrastructure and a tech-savvy population. Protecting customer data isn't just a regulatory requirement but a fundamental aspect of maintaining trust and ensuring business continuity.
The consequences of data breaches can be severe, ranging from financial losses to irreparable damage to a company's reputation. Customers are increasingly aware of their privacy rights and expect businesses to safeguard their personal information with the highest level of security. In Singapore, where digital services are integrated into everyday life, the volume of personal data being collected, processed, and stored is immense. This data can include anything from basic contact information to more sensitive details such as financial records and health information.
Moreover, data breaches can lead to significant legal ramifications. Singapore's Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC) has been vigilant in enforcing data protection laws, imposing heavy fines on businesses that fail to comply. For instance, companies like SingHealth have faced substantial penalties for lapses in data security. These incidents serve as stark reminders that no organization is immune to cyber threats and that robust data protection measures are essential.
In addition to regulatory compliance, there is a business imperative to protect data. A company known for its strong data protection practices can differentiate itself in a crowded market, attracting customers who prioritize privacy. On the other hand, a data breach can lead to loss of consumer trust, reduced customer loyalty, and a decline in market share. In extreme cases, businesses may face lawsuits from affected individuals, further compounding the financial and reputational damage.
The importance of data protection also extends to internal operations. Employees need to be assured that their personal information is handled securely, which can contribute to a positive workplace environment. Furthermore, secure data practices help in safeguarding intellectual property and proprietary business information, which are critical assets for any company.
Finally, it's worth noting that data protection is not just about compliance and risk mitigation; it's also about ethics and corporate responsibility. Businesses have a moral obligation to protect the privacy of their customers and employees. This responsibility entails adopting a proactive approach to data security, staying informed about emerging threats, and continuously improving data protection measures.
In summary, the importance of data protection in Singapore cannot be overstated. It's a multifaceted issue that impacts legal compliance, customer trust, business reputation, operational efficiency, and corporate ethics. As the digital landscape evolves, businesses must remain vigilant and committed to protecting personal data, ensuring they not only meet regulatory requirements but also uphold the highest standards of data security and privacy.

B. Brief Overview of the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA)
The Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) is the cornerstone of Singapore's data protection framework. Enacted in 2012 and enforced by the Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC), the PDPA aims to regulate the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data by organizations, ensuring that individuals' privacy rights are respected and protected.
The PDPA is comprehensive in scope, applying to all private sector organizations, regardless of size or industry. It sets out clear guidelines and principles that businesses must follow to ensure the responsible handling of personal data. The Act is structured around a set of key obligations that organizations must adhere to, which collectively aim to create a robust data protection regime.
One of the fundamental principles of the PDPA is the requirement for organizations to obtain consent before collecting, using, or disclosing personal data. This Consent Obligation is designed to empower individuals, giving them control over their personal information. Organizations must ensure that consent is obtained in a clear and informed manner, and individuals must be aware of the purposes for which their data is being collected.
Another critical aspect of the PDPA is the Purpose Limitation Obligation, which mandates that personal data should only be used for purposes that have been disclosed to the individual and to which they have consented. This obligation prevents organizations from using data for unrelated or unauthorized purposes, thereby protecting individuals from misuse of their personal information.
The PDPA also emphasizes the importance of data accuracy and protection. The Accuracy Obligation requires organizations to make reasonable efforts to ensure that personal data is accurate and complete. Meanwhile, the Protection Obligation mandates that organizations implement reasonable security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, collection, use, disclosure, copying, modification, disposal, or similar risks.
In addition to these obligations, the PDPA includes provisions for data access and correction. Individuals have the right to request access to their personal data and to correct any inaccuracies. Organizations must respond to such requests in a timely manner, ensuring transparency and accountability in their data handling practices.
The PDPA also addresses the issue of data retention, requiring organizations to cease retention of personal data when it is no longer necessary for the purposes for which it was collected. This Retention Limitation Obligation helps minimize the risk of data breaches and ensures that personal data is not kept indefinitely without justification.
The Transfer Limitation Obligation is another key component of the PDPA. It stipulates that personal data transferred outside of Singapore must be accorded a comparable level of protection. This ensures that the privacy rights of individuals are maintained even when their data is processed in other jurisdictions.
The PDPA has undergone several updates and amendments to address evolving data protection challenges. Recent changes include the introduction of mandatory data breach notification requirements and the enhancement of financial penalties for non-compliance. These updates reflect the PDPC's commitment to maintaining a robust and relevant data protection framework in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
In conclusion, the PDPA provides a comprehensive and structured approach to data protection in Singapore. By adhering to the principles and obligations outlined in the Act, organizations can ensure they handle personal data responsibly, protect individuals' privacy rights, and mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and non-compliance.

C. Consequences of Non-Compliance and Penalties
Non-compliance with the PDPA can lead to severe and far-reaching consequences for organizations. The Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC), the regulatory body responsible for enforcing the PDPA, has the authority to impose significant penalties on organizations that fail to adhere to the Act's requirements. These penalties can be financial, operational, and reputational, making it imperative for businesses to prioritize compliance.
One of the most immediate and tangible consequences of non-compliance is the imposition of financial penalties. The PDPC can levy fines of up to S$1 million or 10% of an organization's annual turnover in Singapore, whichever is higher. These fines are not just punitive but also serve as a deterrent to encourage compliance. For many businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, such financial penalties can be crippling, affecting their bottom line and financial stability.
Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance can result in significant operational disruptions. The PDPC has the authority to issue directions to organizations to take remedial actions. These directions can include requirements to stop collecting, using, or disclosing personal data, to destroy data collected in contravention of the PDPA, or to implement specific measures to comply with the Act. Complying with these directions can be resource-intensive, requiring substantial time, effort, and financial investment to rectify non-compliance issues.
The reputational damage resulting from non-compliance can be even more detrimental. Publicized data breaches or PDPC enforcement actions can severely tarnish an organization's reputation, eroding customer trust and confidence. In today's digital age, news of data breaches spreads rapidly, and consumers are quick to lose trust in organizations that fail to protect their personal information. This loss of trust can lead to a decline in customer loyalty, reduced market share, and long-term brand damage.
In addition to financial and reputational consequences, non-compliance can also lead to legal ramifications. Affected individuals have the right to seek recourse through the courts, potentially resulting in costly and protracted legal battles. These legal challenges can further strain an organization's resources and divert attention away from core business activities.
Non-compliance can also have broader implications for business relationships. Partners, vendors, and other stakeholders may be reluctant to engage with organizations that have a history of data protection failures. This can lead to the loss of valuable business opportunities and partnerships, further impacting an organization's growth and success.
The consequences of non-compliance extend beyond immediate penalties and operational disruptions. Long-term impacts include increased scrutiny from regulators, the need for ongoing compliance monitoring, and the implementation of enhanced data protection measures to prevent future breaches. These ongoing efforts can be costly and resource-intensive, placing a continued burden on the organization.
In summary, the consequences of non-compliance with the PDPA are multifaceted and severe. Organizations can face substantial financial penalties, operational disruptions, reputational damage, legal challenges, and strained business relationships. To avoid these consequences, businesses must prioritize data protection, implement robust compliance measures, and foster a culture of accountability and transparency. By doing so, they can protect their customers' personal data, maintain trust, and ensure long-term success in an increasingly regulated digital landscape.

A. Key Definitions
To effectively navigate the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) and ensure compliance, it's crucial to understand the key definitions outlined in the Act. These definitions form the foundation of the PDPA and provide clarity on the scope and application of its provisions.
Understanding these key definitions is critical for organizations to navigate the PDPA effectively. By grasping the scope and implications of personal data, data controllers, data processors, processing, consent, and purpose, businesses can ensure that their data handling practices align with the PDPA's requirements. This foundational knowledge enables organizations to implement robust data protection measures, maintain compliance, and protect individuals' privacy rights in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
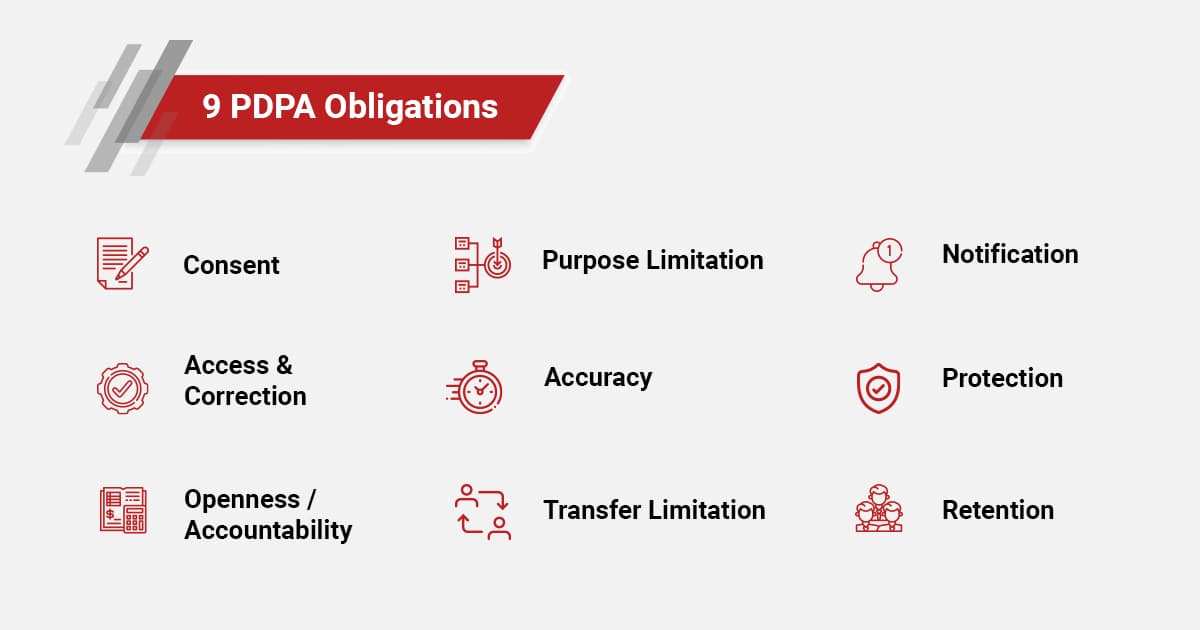
B. The Nine Main Obligations Under the PDPA
The Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) sets out nine key obligations that organizations must adhere to in order to ensure the responsible handling of personal data. These obligations provide a comprehensive framework for data protection and are designed to safeguard individuals' privacy while enabling organizations to manage personal data effectively.
1. Consent Obligation: Organizations must obtain individuals' consent before collecting, using, or disclosing their personal data. Consent must be informed, clear, and voluntary. This means that individuals must be made aware of the purposes for which their data is being collected and must have the option to withdraw their consent at any time. Ensuring explicit consent helps build trust and transparency between organizations and individuals.
2. Purpose Limitation Obligation: Personal data should only be collected, used, or disclosed for purposes that a reasonable person would consider appropriate under the circumstances. Organizations must inform individuals of the specific purposes for which their data is being collected and ensure that the data is not used for any other purpose without obtaining additional consent. This obligation ensures that personal data is used in a manner consistent with individuals' expectations.
3. Notification Obligation: Organizations must notify individuals of the purposes for which their personal data is being collected, used, or disclosed at or before the time of collection. This includes providing clear and comprehensive information about how the data will be handled and the individuals' rights regarding their data. Transparency in data collection practices helps individuals make informed decisions about their personal data.
4. Access and Correction Obligation: Individuals have the right to access their personal data held by an organization and to request corrections to any inaccuracies. Organizations must provide individuals with access to their data upon request and correct any erroneous or incomplete information. This obligation ensures that individuals have control over their personal data and can ensure its accuracy.
5. Accuracy Obligation: Organizations must make reasonable efforts to ensure that personal data collected is accurate and complete. This includes verifying data at the time of collection and periodically reviewing and updating it. Maintaining accurate data is essential for making informed business decisions and providing reliable services to individuals.
6. Protection Obligation: Organizations must implement reasonable security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, collection, use, disclosure, copying, modification, disposal, or similar risks. This includes both technical and organizational measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments. Ensuring robust data protection measures helps prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
7. Retention Limitation Obligation: Personal data should not be retained longer than necessary for the purposes for which it was collected. Organizations must establish and enforce data retention policies, ensuring that data is securely deleted or anonymized when it is no longer needed. This obligation helps minimize the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with data protection principles.
8. Transfer Limitation Obligation: When transferring personal data outside of Singapore, organizations must ensure that the receiving party provides a comparable level of data protection. This includes implementing appropriate safeguards, such as contractual clauses, to protect the data during transfer. Ensuring adequate protection for cross-border data transfers is crucial in an increasingly globalized digital economy.
9. Accountability Obligation: Organizations must be able to demonstrate compliance with the PDPA. This includes appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO), implementing data protection policies and procedures, conducting regular audits and assessments, and maintaining comprehensive records of data processing activities. Demonstrating accountability is essential for building trust with individuals and regulators.
These nine obligations provide a comprehensive framework for data protection, ensuring that organizations handle personal data responsibly and transparently. By adhering to these obligations, businesses can protect individuals' privacy rights, mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, and maintain compliance with the PDPA. Implementing these obligations requires a proactive and systematic approach to data protection, involving continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement of data handling practices.

C. Recent Updates and Amendments to the PDPA
The Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) is a dynamic piece of legislation that evolves to address emerging data protection challenges and align with international standards. Recent updates and amendments to the PDPA have introduced significant changes aimed at enhancing data protection measures, improving accountability, and providing individuals with greater control over their personal data.
In conclusion, the recent updates and amendments to the PDPA reflect the evolving data protection landscape and the need for robust and adaptive regulatory frameworks. These changes enhance data protection measures, improve accountability, and provide individuals with greater control over their personal data. By staying informed about these updates and implementing the necessary measures, organizations can ensure compliance with the PDPA, protect individuals' privacy rights, and navigate the complexities of the digital age effectively.

A. Conducting a Data Inventory and Mapping Exercise
Conducting a data inventory and mapping exercise is a crucial first step in securing customer data and ensuring compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA). This process involves identifying, cataloging, and mapping all personal data within an organization. By understanding what data is collected, where it is stored, and how it flows through the organization, businesses can implement effective data protection measures and mitigate risks.
In conclusion, conducting a data inventory and mapping exercise is a critical best practice for securing customer data and ensuring compliance with the PDPA. By identifying, cataloging, and mapping personal data, organizations can implement effective data protection measures, mitigate risks, and maintain compliance with data protection regulations. This process requires ongoing effort, stakeholder engagement, and a commitment to fostering a culture of data protection within the organization.

B. Implementing Data Protection Policies and Procedures
Implementing robust data protection policies and procedures is essential for safeguarding customer data and ensuring compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA). These policies and procedures provide a framework for how personal data should be handled within the organization, helping to mitigate risks and protect individuals' privacy rights.
In conclusion, implementing robust data protection policies and procedures is essential for securing customer data and ensuring compliance with the PDPA. By developing comprehensive policies, defining clear procedures, and fostering a culture of data protection, organizations can protect personal data, mitigate risks, and maintain trust with their customers. Continuous monitoring, training, and review are critical for ensuring that data protection practices remain effective and aligned with regulatory requirements.

C. Encrypting Sensitive Data and Using Secure Storage Solutions
Encrypting sensitive data and using secure storage solutions are critical components of a robust data protection strategy. These measures help safeguard personal data from unauthorized access, ensuring compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) and protecting individuals' privacy rights.
In conclusion, encrypting sensitive data and using secure storage solutions are essential best practices for securing customer data and ensuring compliance with the PDPA. By implementing robust encryption, access controls, regular security assessments, and comprehensive security policies, organizations can protect personal data from unauthorized access and data breaches. Employee training and awareness are also crucial for maintaining a strong security posture and safeguarding individuals' privacy rights.

D. Controlling Access to Personal Data
Controlling access to personal data is paramount in ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive information. Organizations must implement stringent access control measures to limit the risk of unauthorized data exposure, thereby complying with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) and safeguarding customer trust.
In conclusion, controlling access to personal data is a fundamental aspect of data security and compliance with the PDPA. By implementing robust access control measures such as RBAC, MFA, PoLP, and regular audits, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized data access. Additionally, developing clear access control policies, using advanced access management tools, and providing ongoing security training for employees are crucial for maintaining a secure data environment. These practices not only protect sensitive information but also enhance customer trust and ensure regulatory compliance.
E. Regular Staff Training and Awareness Programs
Regular staff training and awareness programs are critical for ensuring that employees understand their roles and responsibilities in protecting personal data. By fostering a culture of data protection within the organization, businesses can better safeguard sensitive information and comply with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA).
In conclusion, regular staff training and awareness programs are essential for ensuring that employees understand their roles in protecting personal data and complying with the PDPA. By implementing comprehensive, interactive, and role-specific training programs, organizations can foster a culture of data protection awareness and preparedness. Regular updates, real-life examples, and continuous feedback contribute to the effectiveness of these programs, ultimately enhancing the organization’s data protection efforts and ensuring regulatory compliance.

A. Developing an Incident Response Plan
Developing an incident response plan is a critical step in preparing for potential data breaches and ensuring a swift and effective response. An incident response plan outlines the procedures and actions that an organization should take in the event of a data breach or security incident, helping to minimize the impact and ensure compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA).
Establishing an Incident Response Team (IRT): The first step in developing an incident response plan is to establish an Incident Response Team (IRT) composed of individuals with the necessary skills and expertise to handle data breaches. The IRT should include representatives from various departments, such as IT, legal, compliance, communications, and senior management. This cross-functional team ensures a comprehensive approach to incident response, covering all aspects of the breach.
Defining Incident Types and Severity Levels: The incident response plan should clearly define different types of security incidents and categorize them based on their severity. This classification helps the IRT prioritize their response efforts and allocate resources effectively. For example, incidents involving the unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive personal data may be classified as high-severity incidents requiring immediate attention, while minor policy violations may be considered low-severity incidents.
Establishing Incident Detection and Reporting Procedures: Early detection and reporting of incidents are crucial for minimizing the impact of a data breach. The incident response plan should outline the procedures for detecting and reporting incidents, including the tools and technologies used for monitoring and alerting. Employees should be trained to recognize potential security incidents and report them promptly to the IRT. Clear reporting channels and escalation procedures help ensure that incidents are addressed quickly and effectively.
Incident Response Procedures: The plan should detail the specific steps the IRT will take in response to different types of incidents. These procedures should include:
Testing and Drills: Regularly testing the incident response plan through drills and simulations is essential for ensuring that the IRT and other relevant personnel are prepared to respond effectively to real incidents. These exercises help identify gaps in the plan, improve coordination among team members, and enhance overall incident response capabilities.
Post-Incident Review and Improvement: After an incident has been resolved, conducting a thorough post-incident review helps identify lessons learned and areas for improvement. The review should involve all members of the IRT and other relevant stakeholders, focusing on what went well, what could have been done better, and any changes needed to the incident response plan. Continuous improvement of the plan based on these reviews helps organizations better prepare for future incidents.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is a critical aspect of incident response. The plan should outline the specific obligations under the PDPA, including notification requirements and timelines. Organizations should also consider any industry-specific regulations or contractual obligations that may apply.
Communication with External Parties: Effective communication with external parties, such as customers, regulatory authorities, and the media, is crucial during a data breach. The incident response plan should include communication strategies and templates to ensure consistent and timely messaging. Transparent and accurate communication helps maintain trust and manage the organization’s reputation.
In conclusion, developing a robust incident response plan is essential for effectively handling data breaches and minimizing their impact. By establishing an Incident Response Team, defining incident types and severity levels, and outlining detailed response procedures, organizations can ensure a swift and coordinated response to security incidents. Regular testing, post-incident reviews, and compliance with legal requirements further enhance the effectiveness of the incident response plan, ultimately protecting personal data and maintaining regulatory compliance.

B. Notifying Authorities and Affected Individuals
Notifying authorities and affected individuals in the event of a data breach is a critical component of an effective incident response plan. Prompt and transparent notification helps ensure compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) and other relevant regulations, while also maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders.
Regulatory Notification Requirements: The PDPA requires organizations to notify the Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC) of a data breach that is likely to result in significant harm to affected individuals or if the breach is of a significant scale. The notification must be made as soon as practicable, and no later than 72 hours after becoming aware of the breach. The notification should include details of the breach, the types of personal data involved, the number of affected individuals, and the measures taken to address the breach.
Criteria for Notifying Affected Individuals: Organizations are also required to notify affected individuals if the data breach is likely to result in significant harm. Significant harm can include financial loss, identity theft, loss of confidentiality, or other serious consequences. The notification should be made as soon as practicable and should provide clear and concise information about the breach, the types of personal data involved, the potential risks, and the steps affected individuals can take to protect themselves.
Content of Notification to Affected Individuals: The notification to affected individuals should be written in plain language and include the following information:
Communication Channels: Choosing the appropriate communication channels for notifying affected individuals is crucial for ensuring that the message is received promptly. Common channels include email, postal mail, SMS, or direct phone calls. The choice of channel may depend on the nature of the breach, the urgency of the notification, and the organization’s prior communications with the affected individuals.
Handling Media and Public Inquiries: In the event of a high-profile data breach, organizations may also need to manage media and public inquiries. Having a prepared media response plan and designated spokesperson can help ensure consistent and accurate messaging. Transparent communication with the media can help manage the organization’s reputation and provide reassurance to the public.
Coordinating with Third Parties: If the data breach involves third-party service providers or business partners, it is essential to coordinate the notification process with them. This ensures that all parties involved are aligned in their response efforts and that affected individuals receive accurate and consistent information. Data processing agreements with third-party service providers should include provisions for notification and cooperation in the event of a data breach.
Maintaining Records of Notifications: Keeping detailed records of all notifications made to authorities and affected individuals is important for regulatory compliance and post-incident analysis. These records should include the dates and content of notifications, the communication channels used, and any responses received. Documentation helps demonstrate the organization’s compliance with notification requirements and provides valuable information for future reference.
Providing Ongoing Support: After the initial notification, organizations should continue to support affected individuals by providing updates on the investigation and any additional measures taken. Establishing a dedicated support line or helpdesk can assist affected individuals with their concerns and questions. Ongoing communication helps maintain trust and demonstrates the organization’s commitment to addressing the breach.
Training and Preparedness: Ensuring that the Incident Response Team and other relevant personnel are trained in the notification procedures is essential for a swift and effective response. Regular training and simulations can help prepare the team to handle real incidents and ensure that they are familiar with the notification requirements and processes.
In conclusion, notifying authorities and affected individuals promptly and transparently is a crucial aspect of handling data breaches and incidents. By adhering to regulatory requirements, providing clear and timely notifications, and offering ongoing support, organizations can effectively manage the impact of data breaches and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders. Coordination with third parties, maintaining detailed records, and ongoing training further enhance the organization’s ability to respond to data breaches and ensure regulatory compliance.

C. Mitigating the Impact of a Data Breach
Mitigating the impact of a data breach involves taking swift and effective actions to contain the breach, minimize damage, and prevent future incidents. Organizations must have a comprehensive plan in place to address the immediate aftermath of a breach and implement measures to reduce its impact on affected individuals and the organization itself.
Immediate Containment Measures: Upon discovering a data breach, the first priority is to contain the incident to prevent further data loss or unauthorized access. Immediate containment measures can include:
Assessment of the Breach: Conducting a thorough assessment of the breach is essential for understanding its scope and impact. The assessment should involve:
Notification and Support for Affected Individuals: Promptly notifying affected individuals and providing support can help mitigate the impact of the breach. Organizations should:
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is critical in the aftermath of a data breach. Organizations should:
Implementing Long-Term Security Measures: To prevent future incidents and enhance overall data security, organizations should implement long-term security measures, including:
Employee Training and Awareness: Ensuring that employees are aware of data protection best practices and their roles in maintaining data security is crucial. Organizations should:
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement: Continuous monitoring and improvement of data protection practices are essential for maintaining a robust security posture. Organizations should:
In conclusion, mitigating the impact of a data breach requires a coordinated and comprehensive response. By implementing immediate containment measures, conducting thorough assessments, providing support to affected individuals, and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, organizations can effectively manage the aftermath of a breach. Long-term security measures, employee training, and continuous improvement further enhance the organization’s ability to prevent future incidents and protect personal data.

D. Conducting Post-Incident Reviews and Implementing Improvements
Conducting post-incident reviews and implementing improvements is a crucial step in strengthening an organization’s data protection practices and preventing future data breaches. These reviews provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the incident response and highlight areas for enhancement. By systematically analyzing incidents and making necessary adjustments, organizations can build a more resilient data protection framework.
Purpose of Post-Incident Reviews: The primary purpose of post-incident reviews is to learn from the data breach and identify opportunities for improvement. This process involves:
Conducting the Post-Incident Review: A comprehensive post-incident review involves the following steps:
Implementing Improvements: Based on the findings of the post-incident review, organizations should implement improvements to enhance their data protection practices and incident response capabilities. This involves:
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement: Data protection is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Organizations should:
Role of Leadership: Leadership plays a vital role in driving continuous improvement in data protection practices. Senior management should:
In conclusion, conducting post-incident reviews and implementing improvements is essential for enhancing an organization’s data protection practices and preventing future breaches. By systematically analyzing incidents, identifying root causes, and implementing targeted improvements, organizations can build a more resilient data protection framework. Continuous monitoring, regular testing, and strong leadership support further strengthen the organization’s ability to protect personal data and respond effectively to security incidents.

A. Due Diligence When Selecting Service Providers
Engaging third-party service providers can significantly enhance an organization's operations and efficiency. However, it also introduces risks to data protection and security, making due diligence essential when selecting service providers. Ensuring that third parties adhere to the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) and maintain robust data protection practices is critical for safeguarding customer data and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Assessing Data Protection Practices: When selecting a service provider, organizations should conduct a thorough assessment of the provider’s data protection practices. This involves evaluating their policies, procedures, and technologies for handling personal data. Key areas to consider include:
Security Certifications and Standards: Verifying that the service provider complies with recognized security standards and holds relevant certifications can provide assurance of their data protection capabilities. Common certifications and standards to look for include:
Reviewing Data Processing Agreements (DPAs): A Data Processing Agreement (DPA) is a legally binding document that outlines the responsibilities of the service provider and the organization regarding data protection. Key elements of a DPA include:
Conducting Risk Assessments: Performing a risk assessment of the service provider helps identify potential risks to data protection and evaluate the provider’s ability to mitigate those risks. This process involves:
Ongoing Monitoring and Review: Due diligence does not end with the selection of a service provider. Continuous monitoring and regular reviews are essential to ensure that the provider maintains high data protection standards. This involves:
Training and Awareness: Ensuring that employees involved in selecting and managing service providers are trained in data protection principles and aware of their responsibilities is crucial. Training programs should cover:
In conclusion, due diligence when selecting service providers is essential for ensuring that personal data is adequately protected and that the organization complies with the PDPA. By assessing data protection practices, verifying security certifications, reviewing Data Processing Agreements, conducting risk assessments, and maintaining ongoing monitoring and review, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with third-party service providers. Employee training and awareness further support the due diligence process, helping organizations make informed decisions and maintain robust data protection practices.
B. Ensuring Compliance with Data Processing Agreements
Ensuring compliance with Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) is critical for maintaining data protection standards and fulfilling legal obligations under the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA). A well-structured DPA outlines the responsibilities of both the organization and the service provider, helping to safeguard personal data and manage risks associated with data processing activities. This section details the key aspects of ensuring compliance with DPAs.
Understanding the DPA Terms and Conditions: To ensure compliance, organizations must have a thorough understanding of the terms and conditions outlined in the DPA. Key elements to focus on include:
Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting regular audits and assessments of the service provider’s data protection practices is essential for ensuring ongoing compliance with the DPA. This involves:
Monitoring Security Measures: Continuous monitoring of the service provider’s security measures helps ensure that personal data remains protected. This includes:
Managing Data Subject Requests: Ensuring that the service provider can effectively manage data subject requests is crucial for compliance with the PDPA. This involves:
Incident Response Coordination: Coordinating incident response efforts with the service provider is critical for managing data breaches and minimizing their impact. This involves:
Contractual Enforcement: Enforcing the terms of the DPA through contractual mechanisms is essential for maintaining compliance. This includes:
Training and Awareness: Ensuring that employees involved in managing service providers are trained in DPA compliance and data protection principles is crucial. Training programs should cover:
Continuous Improvement: Data protection is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Organizations should:
In conclusion, ensuring compliance with Data Processing Agreements is essential for maintaining data protection standards and fulfilling legal obligations under the PDPA. By understanding the terms of the DPA, conducting regular audits and assessments, monitoring security measures, managing data subject requests, coordinating incident response efforts, enforcing contractual obligations, and providing training and awareness, organizations can effectively safeguard personal data and mitigate the risks associated with third-party service providers. Continuous improvement further enhances the organization’s ability to protect personal data and respond to security incidents.

C. Monitoring and Auditing Service Providers
Ensuring the security of customer data does not end once a third-party service provider is selected. Continuous monitoring and auditing of service providers are essential to maintain data protection standards and compliance with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA). Regular oversight ensures that service providers uphold their contractual obligations and adapt to new security challenges.
Establishing a Monitoring Framework: A robust monitoring framework helps organizations continuously oversee the data protection practices of their service providers. This involves:
Conducting Regular Audits: Regular audits help verify that service providers maintain high data protection standards and comply with the terms of the DPA. This process includes:
Reviewing Security Controls: Continuous review of the service provider’s security controls helps identify potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. This includes:
Incident Management Oversight: Effective incident management oversight ensures that service providers respond appropriately to data breaches and security incidents. This involves:
Ongoing Compliance Checks: Regular compliance checks help ensure that service providers remain aligned with evolving data protection regulations and industry standards. This includes:
Training and Awareness Programs: Providing training and awareness programs for both internal staff and service providers is crucial for maintaining data protection standards. This involves:
Continuous Improvement: Data protection is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Organizations should:
In conclusion, monitoring and auditing service providers are essential components of a comprehensive data protection strategy. By establishing a robust monitoring framework, conducting regular audits, reviewing security controls, overseeing incident management, performing compliance checks, providing training and awareness programs, and continuously improving data protection practices, organizations can effectively safeguard customer data and maintain compliance with the PDPA. Continuous oversight and collaboration with service providers ensure that data protection standards are upheld and that customer data remains secure.

A. Keeping Up with Regulatory Updates and Guidance
The data protection landscape is constantly evolving, with new regulations, amendments, and best practices emerging regularly. Staying compliant in this changing environment requires organizations to remain vigilant and proactive in monitoring regulatory updates and guidance. This section outlines the strategies and steps necessary to stay compliant with the PDPA and other relevant data protection regulations.
Understanding Regulatory Bodies: Organizations should be aware of the regulatory bodies and authorities responsible for data protection oversight. In Singapore, the primary regulatory authority is the Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC). Understanding the role and guidance of the PDPC is essential for compliance.
Monitoring Regulatory Updates: Keeping up with regulatory updates involves:
Analyzing Regulatory Changes: When new regulations or amendments are introduced, organizations should analyze their impact on existing data protection practices. This involves:
Updating Policies and Procedures: Regularly updating data protection policies and procedures is crucial for maintaining compliance. This includes:
Training and Awareness: Providing ongoing training and raising awareness about regulatory changes are essential for ensuring that employees understand their responsibilities and comply with data protection requirements. This involves:
Engaging Legal and Compliance Experts: Engaging legal and compliance experts can provide valuable guidance on navigating regulatory changes and ensuring compliance. This includes:
Staying Informed About Global Regulations: In addition to the PDPA, organizations should stay informed about global data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). This involves:
Proactive Compliance Management: Proactive compliance management involves anticipating regulatory changes and preparing for them in advance. This includes:
In conclusion, staying compliant in a changing landscape requires organizations to remain vigilant and proactive in monitoring regulatory updates and guidance. By understanding regulatory bodies, monitoring updates, analyzing regulatory changes, updating policies and procedures, providing training and awareness, engaging legal and compliance experts, staying informed about global regulations, and proactively managing compliance, organizations can effectively navigate the evolving data protection landscape and maintain compliance with the PDPA and other relevant regulations.
B. Conducting Regular Compliance Audits and Assessments
Regular compliance audits and assessments are fundamental components of maintaining data protection compliance under the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA). These activities help organizations identify gaps, assess risks, and implement necessary improvements to ensure ongoing adherence to regulatory requirements. This section delves into the importance of conducting regular compliance audits and assessments and outlines best practices for effective compliance management.
Importance of Compliance Audits: Regular compliance audits serve multiple critical purposes in data protection management:
Best Practices for Conducting Compliance Audits: Effective compliance audits encompass several best practices to maximize their impact and value:
Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement is integral to maintaining effective data protection compliance:
Integration with Governance Frameworks: Integrate compliance audits into broader governance frameworks to ensure alignment with organizational objectives and strategic initiatives. Align audit outcomes with risk management strategies, corporate governance practices, and internal control frameworks.
Conclusion: Conducting regular compliance audits and assessments is indispensable for ensuring ongoing data protection compliance under the PDPA. By identifying compliance gaps, assessing risks, implementing remediation measures, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can uphold data protection standards, mitigate regulatory risks, and demonstrate accountability to stakeholders. Effective compliance management through audits contributes to building trust with customers, enhancing organizational resilience, and maintaining a competitive edge in today’s data-driven landscape.