
PDPA Singapore: Understanding Your Obligations and Rights as a Business Owner
June 10, 2024






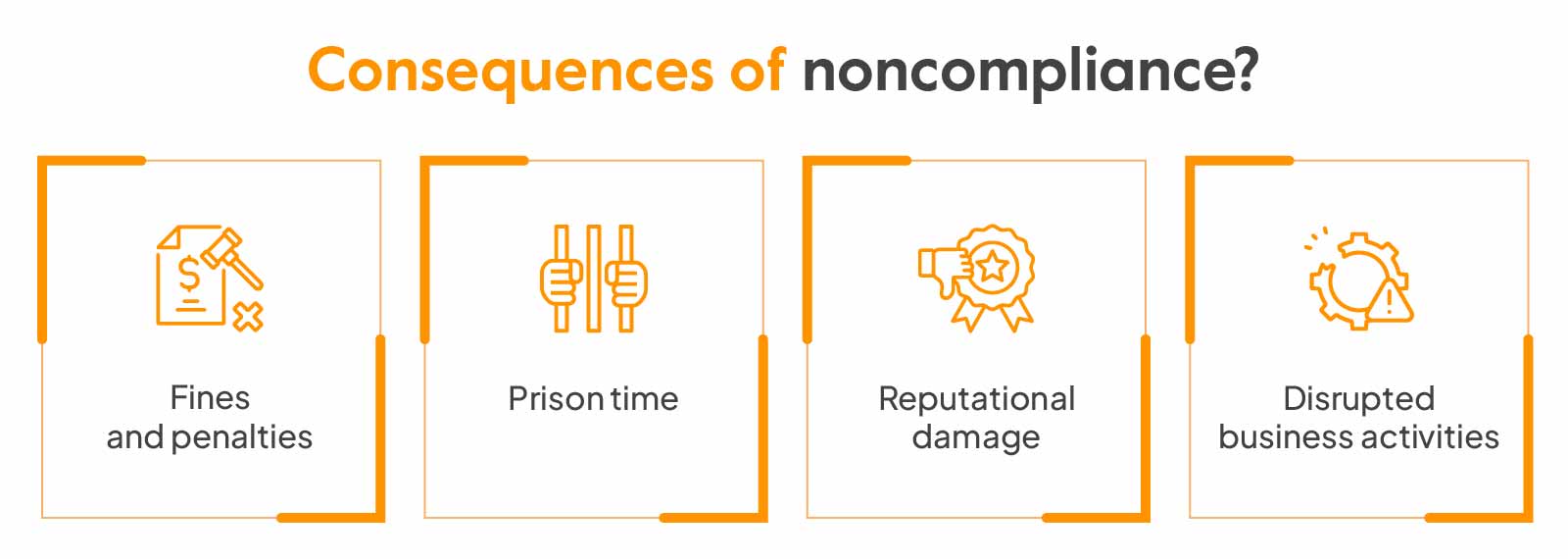 Consequences of Non-Compliance
The consequences of non-compliance with the PDPA are multifaceted. Financial penalties are perhaps the most immediate concern. The Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC) in Singapore has the authority to impose fines up to $1 million SGD for serious breaches. However, the damage doesn't stop at monetary losses. Non-compliance can result in an erosion of customer trust, which is far more costly in the long run. A damaged reputation can lead to lost customers, reduced sales, and a negative impact on brand image. In a world where news spreads like wildfire, a single incident can haunt a company for years.
Moreover, the PDPA is designed to foster a culture of respect and responsibility towards personal data. Organizations that prioritize data protection not only comply with the law but also build a foundation of trust and loyalty with their customers. This trust translates into a competitive advantage, as consumers are more likely to engage with companies that they believe will protect their data.
In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the PDPA, exploring its key principles and obligations. We will also provide actionable best practices for data collection, usage, protection, retention, and disposal, ensuring your organization remains compliant. Furthermore, we will highlight the importance of employee training and working with third-party service providers. Finally, we will discuss the necessity of staying updated with PDPA developments, emphasizing the ongoing commitment required to protect personal data effectively.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
The consequences of non-compliance with the PDPA are multifaceted. Financial penalties are perhaps the most immediate concern. The Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC) in Singapore has the authority to impose fines up to $1 million SGD for serious breaches. However, the damage doesn't stop at monetary losses. Non-compliance can result in an erosion of customer trust, which is far more costly in the long run. A damaged reputation can lead to lost customers, reduced sales, and a negative impact on brand image. In a world where news spreads like wildfire, a single incident can haunt a company for years.
Moreover, the PDPA is designed to foster a culture of respect and responsibility towards personal data. Organizations that prioritize data protection not only comply with the law but also build a foundation of trust and loyalty with their customers. This trust translates into a competitive advantage, as consumers are more likely to engage with companies that they believe will protect their data.
In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the PDPA, exploring its key principles and obligations. We will also provide actionable best practices for data collection, usage, protection, retention, and disposal, ensuring your organization remains compliant. Furthermore, we will highlight the importance of employee training and working with third-party service providers. Finally, we will discuss the necessity of staying updated with PDPA developments, emphasizing the ongoing commitment required to protect personal data effectively.
To effectively comply with the PDPA, it's crucial to understand its fundamental principles and requirements. The PDPA aims to govern the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data by organizations, ensuring that individuals' rights are protected while facilitating the free flow of information for business purposes.
Definition of Personal Data
At the heart of the PDPA is the concept of personal data. According to the PDPA, personal data refers to "data, whether true or not, about an individual who can be identified from that data, or from that data and other information to which the organization has or is likely to have access." This definition is broad and encompasses various forms of data, including but not limited to names, contact information, identification numbers, and even data related to personal preferences and behavior.
Key Principles of the PDPA
The PDPA is built upon several key principles that organizations must adhere to:
Obligations of Organizations under the PDPA
To comply with the PDPA, organizations must fulfill several obligations, including:
By understanding these principles and obligations, organizations can lay a strong foundation for PDPA compliance and protect personal data effectively.

Collecting personal data is a fundamental aspect of many business operations. However, it must be done responsibly and in compliance with the PDPA to protect individuals' privacy and avoid penalties.
Obtain Consent from Individuals
Obtaining consent is a cornerstone of the PDPA. Organizations must ensure that they obtain clear and informed consent from individuals before collecting their personal data. This involves providing individuals with sufficient information about the purposes for which their data will be used and obtaining their explicit agreement. Consent should not be obtained through misleading or coercive means.
To secure consent effectively, organizations can adopt several strategies. Firstly, consent forms should be written in plain language, avoiding legal jargon that might confuse individuals. Including examples and scenarios can help illustrate how the data will be used, making it easier for individuals to understand and agree. Additionally, offering granular consent options allows individuals to choose which types of data they are comfortable sharing, fostering a sense of control and trust.
Provide Clear and Concise Privacy Policies
Transparency is key to building trust with individuals. Organizations should provide clear and concise privacy policies that explain how personal data will be collected, used, disclosed, and protected. These policies should be easily accessible, written in plain language, and regularly updated to reflect any changes in data handling practices.
Privacy policies should cover essential information such as the types of data collected, the purposes of data collection, how the data will be used and shared, and the measures taken to protect the data. Including contact information for the Data Protection Officer (DPO) or another responsible party can provide individuals with a direct point of contact for any concerns or inquiries.
Collect Only Necessary Personal Data
Organizations should adopt a data minimization approach, collecting only the personal data that is necessary for the intended purposes. This not only reduces the risk of data breaches but also demonstrates respect for individuals' privacy. Before collecting any data, organizations should evaluate whether it is essential and consider alternative ways to achieve their objectives without collecting excessive information.
For instance, if a company is conducting a survey, it should carefully design the survey questions to collect only the information needed for the analysis. Avoid asking for sensitive information unless it is absolutely necessary. By focusing on collecting relevant data, organizations can reduce the potential risks associated with data breaches and misuse.
Use Appropriate Data Collection Methods
The methods used to collect personal data should be secure and appropriate for the type of data being collected. Organizations should implement measures to verify the accuracy of the data and ensure that it is collected in a manner that protects individuals' privacy. For example, online forms should be encrypted, and physical documents should be stored securely.
Organizations should also consider the context in which data is collected. For instance, collecting data through a secure online portal is preferable to using paper forms that can be easily lost or stolen. Implementing identity verification processes can help ensure that the data collected is accurate and belongs to the intended individual.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure that their data collection processes are compliant with the PDPA and minimize the risk of data breaches and penalties.

Using personal data responsibly is essential to maintaining compliance with the PDPA and protecting individuals' privacy.
Use Personal Data Only for Intended Purposes
Organizations must use personal data only for the purposes for which it was collected, as specified in the privacy policy and consent obtained from individuals. Using data for unintended purposes without obtaining fresh consent is a violation of the PDPA and can lead to significant penalties.
To ensure compliance, organizations should establish clear internal guidelines and procedures for data usage. These guidelines should outline the specific purposes for which the data can be used and provide examples of prohibited uses. Regular audits and monitoring can help identify and address any deviations from the intended purposes.
Obtain Fresh Consent for New Uses of Data
If an organization wishes to use personal data for new purposes that were not initially disclosed to individuals, it must obtain fresh consent. This involves informing individuals about the new purposes and obtaining their explicit agreement. Organizations should be transparent about why the new use is necessary and how it benefits the individuals.
For example, if a company initially collected data for marketing purposes but later wants to use it for research, it must notify individuals and obtain their consent for this new use. Providing clear explanations and benefits of the new use can help individuals make informed decisions and feel more comfortable granting consent.
Ensure Accuracy and Completeness of Data
Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of personal data is crucial to ensuring that data-driven decisions are based on reliable information. Organizations should implement processes to regularly review and update personal data, correcting any inaccuracies and filling in missing information. This helps to prevent misinformation and protects individuals' rights.
Organizations can use various methods to ensure data accuracy, such as periodic data validation exercises, automated data quality checks, and feedback mechanisms that allow individuals to update their information. By keeping data accurate and complete, organizations can improve the reliability of their operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Limit Access to Personal Data Within the Organization
Access to personal data should be limited to authorized personnel who need it to perform their job duties. Implementing strict access controls and role-based permissions can help ensure that only those with a legitimate need can access sensitive information. Regularly reviewing and updating access permissions can prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Organizations should also implement logging and monitoring mechanisms to track access to personal data. This can help identify any unauthorized access attempts and provide insights into data usage patterns. By limiting access and monitoring data usage, organizations can enhance the security of personal data and reduce the risk of breaches.
By following these best practices for data usage, organizations can ensure that they use personal data responsibly and in compliance with the PDPA. This not only helps protect individuals' privacy but also builds trust and credibility with customers.
Protecting personal data is a critical aspect of PDPA compliance. Organizations must implement robust security measures to safeguard personal data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other risks.
Implement Robust Security Measures
Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other risks. This includes physical, technical, and administrative safeguards. For instance, encryption can be used to protect data stored on devices and transmitted over networks, while access controls can limit who can view or modify the data. Regularly updating and patching systems can also help protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keeping systems up to date is crucial for protecting against security vulnerabilities. Organizations should establish a regular schedule for updating and patching software, operating systems, and applications. This helps ensure that any known security flaws are addressed promptly, reducing the risk of exploitation by malicious actors.
In addition to regular updates, organizations should also consider implementing automated patch management solutions. These solutions can streamline the process of identifying, downloading, and applying patches, ensuring that systems remain secure without requiring manual intervention.
Conduct Risk Assessments and Audits
Regular risk assessments and audits are essential for identifying and mitigating potential security risks. Organizations should conduct comprehensive assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of their security measures and identify any weaknesses. This can involve reviewing access controls, encryption methods, and incident response plans.
Risk assessments should be conducted periodically, as well as in response to significant changes in the organization's operations or threat landscape. By proactively identifying and addressing risks, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and protect personal data more effectively.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
Having a robust incident response plan in place is critical for effectively managing data breaches and other security incidents. The plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, including how to identify, contain, and remediate the incident. It should also include procedures for notifying affected individuals and reporting the breach to the relevant authorities, such as the PDPC.
Incident response plans should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the organization's operations and the evolving threat landscape. Conducting regular drills and simulations can help ensure that employees are familiar with the plan and can respond effectively in the event of a real incident.
By implementing these best practices for data protection, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. This not only helps protect personal data but also demonstrates a commitment to compliance with the PDPA and builds trust with customers.

Effective data retention and disposal practices are essential for ensuring compliance with the PDPA and protecting personal data.
Retain Personal Data Only for Necessary Duration
Organizations should retain personal data only for as long as necessary to fulfill the purposes for which it was collected. This involves establishing clear data retention policies that define the duration for which different types of data should be kept. Once the data is no longer needed, it should be securely deleted or anonymized.
To ensure compliance, organizations should regularly review their data retention policies and practices. This can involve conducting periodic data audits to identify any data that is no longer needed and should be disposed of. By retaining data only for the necessary duration, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and protect individuals' privacy.
Securely Dispose of Personal Data When No Longer Needed
Secure disposal of personal data is crucial for preventing unauthorized access and misuse. Organizations should implement secure disposal methods that are appropriate for the type of data being discarded. For example, paper documents containing personal data should be shredded, while digital data should be securely deleted using methods that ensure it cannot be recovered.
In addition to implementing secure disposal methods, organizations should also maintain records of data disposal activities. This helps demonstrate compliance with the PDPA and provides a clear audit trail in the event of any inquiries or investigations.
Maintain Records of Data Disposal
Maintaining records of data disposal activities is an important aspect of demonstrating compliance with the PDPA. These records should include details such as the types of data disposed of, the methods used for disposal, and the dates of disposal. This information can be used to verify that data has been securely deleted and to address any potential concerns about unauthorized access.
Organizations should establish clear procedures for documenting data disposal activities and ensure that these records are stored securely. Regular reviews of disposal records can help identify any gaps or inconsistencies and ensure that data disposal practices remain compliant with the PDPA.
By following these best practices for data retention and disposal, organizations can ensure that personal data is managed responsibly and in compliance with the PDPA. This helps protect individuals' privacy and reduces the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Educating employees about data protection is essential for ensuring compliance with the PDPA and fostering a culture of privacy within the organization.
Educate Employees on PDPA Requirements
Organizations should provide comprehensive training to employees on PDPA requirements and best practices for data protection. This training should cover key topics such as the definition of personal data, the principles of the PDPA, and the specific obligations of employees. By ensuring that employees understand their responsibilities, organizations can reduce the risk of non-compliance and data breaches.
Training programs should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of employees. For example, employees who handle personal data directly should receive more detailed training on data collection, usage, and protection practices. Regular refresher training can help reinforce key concepts and keep employees updated on any changes to the PDPA or internal policies.
Provide Regular Training and Updates
Data protection is an ongoing effort, and organizations should provide regular training and updates to ensure that employees remain informed about the latest best practices and regulatory requirements. This can involve conducting periodic training sessions, sharing updates through internal communications, and providing access to relevant resources and materials.
Organizations should also consider incorporating data protection topics into existing training programs, such as onboarding for new employees and annual compliance training. This helps to embed a culture of data protection within the organization and ensures that all employees are aware of their responsibilities.
Foster a Culture of Data Protection Within the Organization
Creating a culture of data protection requires more than just training; it involves fostering a mindset of privacy and responsibility throughout the organization. This can be achieved by integrating data protection into the organization's values, policies, and practices. Leadership should play a key role in promoting the importance of data protection and setting an example for employees to follow.
Organizations can also encourage employees to take an active role in data protection by recognizing and rewarding good practices. For example, employees who identify and report potential data protection risks or who demonstrate exceptional compliance with PDPA requirements can be acknowledged through internal recognition programs.
Conduct Data Protection Awareness Campaigns
Raising awareness about data protection can be achieved through targeted campaigns and initiatives. Organizations can use various channels to promote data protection messages, such as newsletters, posters, and intranet sites. These campaigns can highlight key aspects of the PDPA, share tips for protecting personal data, and provide information about the organization's data protection policies and practices.
By educating employees and fostering a culture of data protection, organizations can ensure that their staff are equipped to handle personal data responsibly and in compliance with the PDPA. This helps to reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents and demonstrates a commitment to protecting individuals' privacy.

Collaborating with third-party service providers is often necessary for business operations, but it also introduces potential risks to data protection. Organizations must take steps to ensure that their service providers comply with the PDPA and maintain the same level of data protection.
Conduct Due Diligence on Service Providers
Before engaging with third-party service providers, organizations should conduct thorough due diligence to assess their data protection practices. This involves evaluating the provider's security measures, data handling procedures, and compliance with relevant data protection regulations. Organizations should request documentation and evidence of the provider's data protection practices, such as certifications, audit reports, and security policies.
Due diligence should also include assessing the provider's reputation and track record. Organizations can seek references from other clients, review public information, and consider conducting independent assessments to ensure that the provider has a strong commitment to data protection.
Establish Data Protection Agreements
Establishing data protection agreements with third-party service providers is essential for ensuring compliance with the PDPA. These agreements should outline the specific data protection obligations of the provider, including the security measures they must implement, the conditions for data transfer, and the procedures for handling data breaches.
Data protection agreements should also specify the rights and responsibilities of both parties, including the organization's right to audit the provider's data protection practices. Organizations should ensure that these agreements are legally binding and regularly reviewed to reflect any changes in the relationship or the regulatory environment.
Monitor and Audit Service Providers' Data Protection Practices
Ongoing monitoring and auditing of service providers' data protection practices are crucial for ensuring compliance with the PDPA. Organizations should establish regular audit schedules to assess the provider's adherence to the agreed-upon data protection measures. This can involve conducting on-site inspections, reviewing documentation, and performing security assessments.
Organizations should also implement monitoring mechanisms to track the provider's data handling activities and detect any potential issues. This can include logging and analyzing access to personal data, reviewing incident reports, and monitoring compliance with data protection agreements.
Provide Data Protection Training to Service Providers
To ensure that service providers understand their data protection responsibilities, organizations should provide them with relevant training and resources. This can involve sharing information about the PDPA, providing guidance on best practices for data protection, and offering access to training materials and resources.
Organizations should also consider including data protection requirements in their contracts and service-level agreements with providers. This helps to ensure that the provider is aware of their obligations and committed to maintaining a high level of data protection.
By working closely with third-party service providers and ensuring that they comply with the PDPA, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with data sharing and maintain a strong commitment to data protection. This helps to build trust with customers and demonstrate a proactive approach to protecting personal data.

The regulatory landscape for data protection is constantly evolving, and organizations must stay updated with the latest developments to ensure ongoing compliance with the PDPA.
Keep Abreast of Amendments and New Guidelines
The PDPA is subject to amendments and updates to address emerging data protection challenges and align with international standards. Organizations should actively monitor for any changes to the PDPA and related guidelines issued by the PDPC. This involves subscribing to regulatory updates, participating in industry forums, and engaging with legal experts to stay informed about the latest developments.
Organizations should also regularly review their data protection policies and practices to ensure they align with the latest requirements. This can involve conducting gap analyses to identify any areas that need improvement and updating internal procedures to reflect the changes.
Attend Workshops and Seminars
Participating in workshops, seminars, and conferences on data protection can provide valuable insights into the latest trends, best practices, and regulatory updates. These events offer opportunities to learn from experts, network with peers, and gain practical knowledge that can be applied to enhance data protection efforts.
Organizations should encourage their employees, particularly those involved in data protection roles, to attend relevant events and training sessions. This helps to build a culture of continuous learning and ensures that staff are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to manage personal data responsibly.
Engage with Professional Associations and Legal Experts
Engaging with professional associations and legal experts can provide organizations with access to valuable resources, guidance, and support. Professional associations, such as the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), offer a wealth of information on data protection best practices, regulatory updates, and industry trends.
Legal experts can provide tailored advice and support to help organizations navigate complex data protection challenges and ensure compliance with the PDPA. Establishing relationships with legal experts can also provide organizations with access to timely updates and insights into the latest regulatory developments.
Implement Continuous Improvement Practices
Organizations should adopt a mindset of continuous improvement when it comes to data protection. This involves regularly reviewing and updating data protection policies, procedures, and practices to ensure they remain effective and compliant with the latest requirements. Conducting regular audits, risk assessments, and feedback sessions can help identify areas for improvement and drive ongoing enhancements.
By staying updated with PDPA developments and adopting continuous improvement practices, organizations can ensure that they remain compliant with the latest data protection requirements. This helps to protect personal data, build trust with customers, and demonstrate a commitment to privacy and security.
In conclusion, ensuring compliance with the PDPA is crucial for protecting personal data and maintaining trust with customers. By following best practices for data collection, usage, protection, retention, and disposal, organizations can effectively manage personal data and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Recap of Key Best Practices
Importance of Ongoing Commitment to Data Protection
Data protection is an ongoing effort that requires continuous commitment and vigilance. Organizations must stay proactive in their approach to data protection, regularly reviewing and updating their policies and practices to address new challenges and regulatory requirements. By fostering a culture of privacy and responsibility, organizations can protect personal data and maintain trust with their customers.
Benefits of PDPA Compliance for Businesses and Customers
Compliance with the PDPA offers numerous benefits for both businesses and customers. For businesses, it reduces the risk of penalties, enhances reputation, and builds trust with customers. For customers, it ensures that their personal data is handled responsibly and protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
By following the best practices outlined in this blog post, organizations can ensure that they remain compliant with the PDPA, protect personal data effectively, and demonstrate a commitment to privacy and security. This not only helps to build trust and credibility but also supports business growth and success in the digital age.
FAQs
What is the PDPA and why is it important?
The PDPA, or Personal Data Protection Act, is a law in Singapore that governs the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data by organizations. It aims to protect individuals' privacy while allowing for the free flow of information for business purposes. Compliance with the PDPA is important because it helps protect personal data, reduces the risk of penalties, and builds trust with customers.
How can organizations obtain consent for data collection under the PDPA?
Organizations can obtain consent for data collection by providing individuals with clear and sufficient information about the purposes for which their data will be used and obtaining their explicit agreement. Consent forms should be written in plain language and offer granular options to allow individuals to choose which types of data they are comfortable sharing.
What are the key principles of the PDPA that organizations must adhere to?
The key principles of the PDPA include obtaining consent, limiting data collection and usage to specific purposes, ensuring data accuracy and protection, retaining data only for necessary durations, and implementing appropriate security measures. Organizations must also ensure transparency, accountability, and compliance with the PDPA's requirements.